What is Welding Fume, and How Does It Form?
Welding fume generally refers to the smoke and vapors produced during metal welding in the metalworking industry. During the welding process, the electrode, wire, or other welding materials cause the metal to melt and fuse, releasing various gases and fumes in the process.
The composition of welding fumes can vary depending on the materials used, the welding method, and the type of metal being welded. These fumes can pose serious health risks. Therefore, welding operations are typically carried out in well-ventilated areas or with the use of appropriate respiratory protective equipment. Depending on the substances contained in welding fumes, inhalation of these fumes can cause severe respiratory issues.
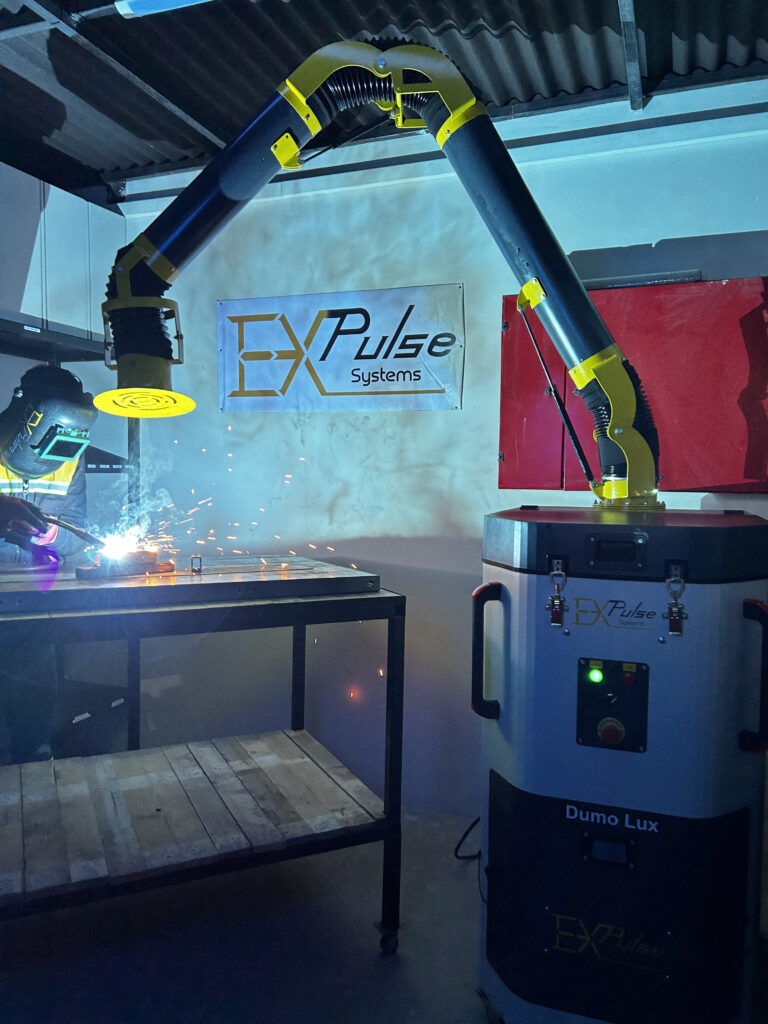
Expulse filtration solutions effectively capture welding fumes and dust, providing 99.9% filtration efficiency. Welding companies trust Expulse’s mobile and central filtration systems for effective fume extraction.
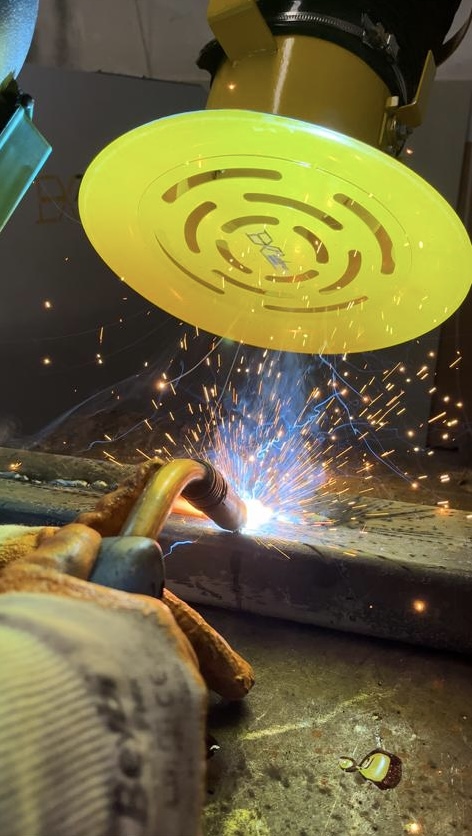

What Are the Components of Welding Fumes?
The pollutants in welding fumes vary based on the welding method, materials used, and process conditions. However, they generally include the following components:
- Metal Oxides: During welding, the metal surface reacts under high heat, oxidizing and forming metal oxides. These oxides are a major component of welding fumes and are generally harmful to health. Common metal oxides include zinc oxide, iron oxide, and lead oxide.
- Acid Gases: The heating of shielding gases or coating materials during welding can produce acid gases, which can harm the respiratory system. Examples include hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen chloride, and hydrogen cyanide.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) and Carbon Monoxide (CO): Combustion reactions during welding can release carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. In enclosed spaces, the accumulation of these gases can cause respiratory issues and poisoning.
- Metal Vapors: The evaporation of metals during welding can release harmful metal vapors, including aluminum, lead, and copper vapors.
- Particles: Welding fumes contain ultrafine particles that can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, potentially causing lung damage.
All of these contaminants can cause respiratory, skin, and overall health issues if exposure is prolonged. That’s why using proper personal protective equipment and working in well-ventilated areas is crucial. Expulse provides ready-to-use mobile products and extraction arms, offering source capture solutions for welding fumes with a wide range of product options.
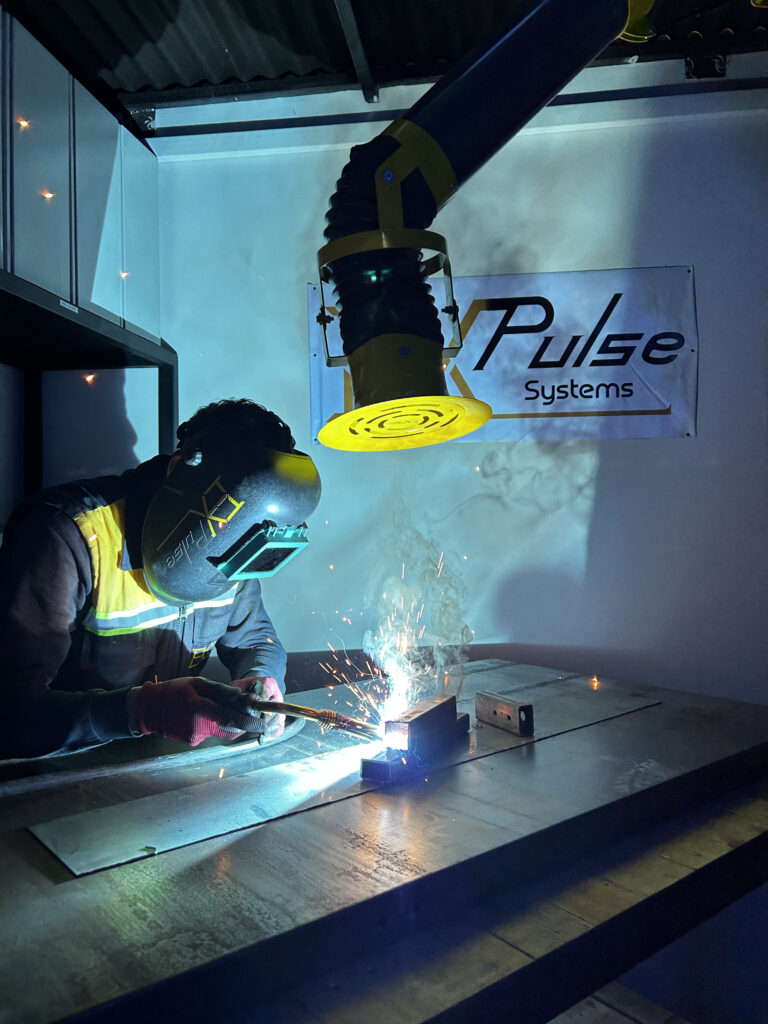

What Are the Particle Sizes of Welding Fumes?
The particle sizes of welding fumes depend on factors such as the type of welding, fuel type, and combustion conditions. Generally, welding fume particles fall within the micro and nano size range, typically between 0.1 to 1 micrometer.
Larger particles can also form, especially in heavy industrial applications, with sizes reaching several micrometers or larger.
Nano and micro-sized particles can travel longer distances and penetrate deeper into the respiratory system, making them more hazardous to human health. Understanding the particle sizes of welding fumes is crucial in assessing their health impact. Expulse filters effectively capture welding particles with 99.9% efficiency.
The table below shows the different particle sizes:
| Particle Type | Size Range | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Nano Particles | 1 nanometer – 100 nanometers | Thousands of times smaller than a human hair |
| Micro Particles | 1 micrometer – 100 micrometers | Close to or slightly larger than the diameter of a human hair |
| Large Particles | 100 micrometers – 10 millimeters | Larger than a human hair, visible to the naked eye |
Welding Fume: The Overlooked Hazard in Industrial Environments
In industrial production, welding fume is often an overlooked factor that carries serious health and environmental risks. Welding fume is a combination of combustible gases, vapors, and particles generated during welding, soldering, cutting, and other similar operations. These fumes contain toxic chemicals that pose significant risks to workers’ health. Additionally, harmful emissions released into the environment contribute to air pollution, negatively impacting public health.
The health risks of welding fume exposure include respiratory illnesses (such as asthma and bronchitis), eye irritation, skin problems, nervous system disorders, and even an increased risk of cancer. Regardless of the level or duration of exposure, implementing protective measures against welding fumes is crucial.
Welding fumes not only affect worker health but also have a major impact on the environment. The toxic emissions released into the atmosphere contribute to air pollution and environmental contamination. Especially in enclosed areas, welding fumes can severely degrade air quality, endangering nearby organisms.
One of the most effective ways to minimize the health and environmental impact of welding fumes is the use of efficient mobile fume extraction units. These units capture and filter welding fumes during operations, ensuring cleaner air. Mobile welding fume extraction units reduce worker exposure to hazardous fumes while minimizing environmental pollution, creating a healthier workplace.
This is where our Dumo series mobile welding fume extraction units come into play. With powerful suction and effective filtration, our Dumo mobile units efficiently collect welding fumes in industrial environments, ensuring worker safety. Additionally, Dumo mobile filtration units feature a compact and portable design, allowing them to be easily moved to different workspaces for flexible use.
Mobile welding fume extraction units enhance health and safety standards in industrial facilities while promoting environmental sustainability. As such, they are an essential investment for industrial businesses.